
Table of Contents
- Cybersecurity
- Malware
- Firewall
- Phishing
- Encryption
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
- Patch
- Cyber Attack
- Data Breach
- Zero-Day Vulnerability
- Social Engineering
- Antivirus
- DDoS Attack
- Vulnerability Assessment
- VPN (Virtual Private Network)
- SSL/TLS
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
- Penetration Testing
- Insider Threat
- Encryption Key
- SIEM (Security Information and Event Management)
- Ransomware
- Network Security
- Malware Analysis
- Cybersecurity Policy
Cybersecurity

Cybersecurity refers to the practice of protecting computer systems, networks, and data from theft, damage, or unauthorized access. It encompasses a range of technologies, processes, and practices designed to safeguard digital information and ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data.
Malware

Malware, short for "malicious software," is software designed to harm, steal, or exploit your data and computer systems. Common types of malware include viruses, worms, Trojans, spyware, adware, and ransomware. Malware can infect your devices and compromise your privacy, making it a significant cybersecurity threat.
Firewall

A firewall is a network security device or software that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic. It acts as a barrier between your internal network and external networks (like the internet) and enforces security rules to allow or block data packets based on predefined criteria. Firewalls are essential for protecting your network from unauthorized access and cyber threats.
Phishing

Phishing is a type of cyber attack where attackers impersonate legitimate entities (such as banks, businesses, or government agencies) to trick individuals into revealing sensitive information like login credentials, credit card numbers, or personal data. Phishing attacks often involve deceptive emails, websites, or messages and are a common method used by cybercriminals.
Encryption

Encryption is the process of converting data into a secure format that can only be read by authorized parties with the appropriate decryption key. It is a fundamental technique for protecting sensitive information during transmission and storage. Encryption ensures the confidentiality and privacy of data, making it unreadable to anyone who doesn't have the encryption key.
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)

Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) is an additional layer of security that requires users to provide two different authentication factors before gaining access to an account or system. The factors typically include something the user knows (e.g., a password) and something the user has (e.g., a smartphone app or hardware token). 2FA enhances security by reducing the risk of unauthorized access, even if passwords are compromised.
Patch

A patch is a software update or fix released by software developers to address vulnerabilities or bugs in their applications or operating systems. Applying patches is crucial for maintaining a secure system, as cybercriminals often exploit known vulnerabilities to launch attacks. Regularly updating software helps protect against security threats.
Cyber Attack

A cyber attack is any deliberate action aimed at compromising the confidentiality, integrity, or availability of computer systems, networks, or data. Cyber attacks can take various forms, including malware infections, data breaches, denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, and social engineering scams. Organizations and individuals must implement robust cybersecurity measures to defend against these threats.
Data Breach

A data breach occurs when unauthorized individuals gain access to sensitive or confidential data. Data breaches can result from cyber attacks, system vulnerabilities, or human error. They can have severe consequences, including financial losses, reputational damage, and legal implications. Protecting against data breaches is a critical aspect of cybersecurity.
Zero-Day Vulnerability

A zero-day vulnerability is a software vulnerability that is unknown to the software vendor or the public. Cybercriminals can exploit these vulnerabilities before a patch or fix becomes available. Zero-day attacks can be highly damaging and challenging to defend against, making rapid vulnerability detection and mitigation crucial.
Social Engineering

Social engineering is a psychological manipulation technique used by cybercriminals to deceive individuals into divulging confidential information or performing actions that compromise security. It often involves impersonating trusted entities, exploiting human psychology, and creating a false sense of urgency. Awareness and education are key defenses against social engineering attacks.
Antivirus

Antivirus software is designed to detect, prevent, and remove malicious software (malware) from computer systems. It scans files and programs for known malware signatures and behaviors, helping to protect against a wide range of threats, including viruses, Trojans, and spyware. Antivirus software should be regularly updated to stay effective against emerging threats.
DDoS Attack

A Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attack is a cyber attack that aims to overwhelm a target's online services or network infrastructure by flooding it with a massive volume of traffic. The goal is to make the targeted services unavailable to users. DDoS attacks can disrupt business operations and require effective mitigation strategies to counteract.
Vulnerability Assessment

A vulnerability assessment is a systematic process of identifying and evaluating weaknesses in an organization's IT infrastructure, applications, and security controls. It helps organizations proactively address security flaws before they can be exploited by attackers. Regular vulnerability assessments are essential for maintaining strong cybersecurity defenses.
VPN (Virtual Private Network)

A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is a technology that provides secure and encrypted connections over unsecured networks, such as the internet. VPNs are used to protect data privacy and security by creating a private network tunnel that shields communication from potential eavesdroppers and cyber threats.
SSL/TLS

SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) and TLS (Transport Layer Security) are cryptographic protocols used to secure data transmission over the internet. They establish encrypted connections between web browsers and servers, ensuring data confidentiality and integrity. SSL/TLS certificates are essential for websites to provide secure HTTPS connections.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)

Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is an authentication method that requires users to provide two or more factors to access an account or system. It enhances security by combining something the user knows (e.g., a password) with something the user has (e.g., a smartphone or hardware token). MFA adds an extra layer of protection against unauthorized access.
Penetration Testing
Penetration testing, often referred to as ethical hacking, is a practice where security professionals simulate cyber attacks on an organization's systems and networks to identify vulnerabilities. The goal is to assess the security posture and discover weaknesses that could be exploited by real attackers. Penetration testing helps organizations strengthen their defenses.
Insider Threat

An insider threat refers to security risks posed by individuals within an organization, such as employees, contractors, or partners, who have access to sensitive information and may misuse it intentionally or unintentionally. Insider threats can be challenging to detect and mitigate, making insider threat programs essential for security.
Encryption Key

An encryption key is a piece of information used to encrypt and decrypt data during the encryption process. It is a critical component of encryption algorithms, and the security of encrypted data depends on the strength and protection of encryption keys. Proper key management is essential for data security.
SIEM (Security Information and Event Management)

SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) is a comprehensive approach to security management that combines security information management (SIM) and security event management (SEM). SIEM systems collect and analyze data from various sources to detect and respond to security incidents. They play a crucial role in monitoring and managing cybersecurity threats.
Ransomware
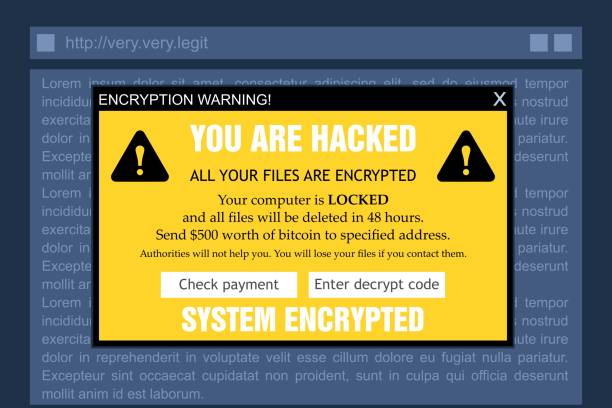
Ransomware is a type of malware that encrypts a victim's files or systems and demands a ransom payment from the victim in exchange for a decryption key. Ransomware attacks can have severe consequences, leading to data loss and financial losses. Prevention and backup strategies are key defenses against ransomware.
Network Security
Network security encompasses the practices, policies, and technologies used to protect a network infrastructure from unauthorized access, data breaches, and cyber attacks. It includes measures such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, access controls, and network monitoring to ensure the security of data in transit and at rest.
Malware Analysis

Malware analysis is the process of examining and dissecting malicious software to understand its functionality, behavior, and impact. Security professionals use malware analysis to identify and develop countermeasures against malware threats. It is a crucial aspect of cybersecurity for threat intelligence and incident response.
Cybersecurity Policy
A cybersecurity policy is a set of guidelines, procedures, and rules that an organization follows to protect its digital assets and information. It defines security practices, responsibilities, and compliance requirements to ensure a consistent and secure approach to cybersecurity within the organization.
Join Our Cybersecurity Community!
Stay updated with the latest cybersecurity trends, tips, and news. Subscribe to our blog and become a part of our wonderful cybersecurity community.
Subscribe Now



0 Comments